There is simply no substitute for the contribution of telecom and communication technologies in industrial automation in this fast-changing technological environment of today. It's changing the very way of working of the industries by the integration of telecom networks, wireless communication systems, and IoT (Internet of Things) solutions. Not only is this making the process more efficient and less expensive to operate but also allowing flexibility, safety, and real-time data analysis in the manufacturing environment. This blog describes how telecom and communication systems enhance industrial automation, their benefits, key technologies, and the future of automation in different sectors.
What is Industrial Automation?
Industrial automation refers to the use of control systems including computers, robots, and information technologies to handle various processes and machinery in an industry without human involvement. Automation increases the efficiency, quality, and production rate of manufacturing and production lines. Industrial automation was previously a wired system of communication, besides being isolated control mechanism. Advanced telecom as well as communication solutions were integrated to get smarter flexible automation systems within the industries because of the demands of connectivity and real-time sharing of data besides management through remote connectivity.
Telecom and Communication in Industrial Automation

Telecom and communication technologies are the spine of modern industrial automation. They provide un-interrupted connection, data transfer, and communications between machines, control systems, and remote operators. The core advantages of telecom and communication in automation are the following:
- Real-time Communication: Communication technologies permit real-time information exchange between the machines, sensors, and the operators. These facilitate better decisions and allow quicker responses to irregularities in a system.
- Remote Monitoring and Control: Advanced telecom networks allow the remote monitoring and control of machinery. This is an important function for large-scale operation where on-site monitoring cannot be feasible.
- Data Transfer and Analytics: Data transfer between industrial equipment and control systems provided is through telecom systems. The data thus acquired is analyzed in order to improve production efficiencies and anticipate maintenance requirements.
- Wireless Connectivity: Wireless communication technologies, such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and 5G, are increasingly used in industrial automation systems. It reduces the dependence on cumbersome wired systems and allows for greater flexibility and ease of deployment.
- Internet of Things (IoT) Integration: IoT is the next industrial automation big thing. IoT devices connected through telecom networks collect and share data from different sensors and machines. This facilitates data-driven decision-making for industries, enhances the efficiency of their operations, and reduces downtime.
Technologies Enhancing Industrial Automation
In particular, several technologies in telecom and communications are pushing the future of industrial automation. Such technologies help develop smarter and more efficient manufacturing processes. Among these are:
1. 5G Networks
It will be the revolution that changes industrial automation with 5G technology. Applications in industries such as automotive manufacturing, oil and gas, and logistics are considered possible because of ultra-low latency, high reliability, and fast data transfer speed that enables real-time communication between machines and control systems. Along with the sheer amounts of MTC, 5G's capabilities enable tremendous machine-type communications (mMTC) so that thousands and thousands of Internet of Things' devices can be connected within one factory or even a whole industrial domain.
2 IoT (Internet of Things)
Internet of Things, or IoT, is defined as a network of devices that could communicate with each other and exchange data. IoT devices are implemented in industrial automation by embedding machinery, sensors, and equipment to gather real-time data, which can be analyzed afterwards in a centralized system. IoT sensors can measure parameters such as temperature, pressure, humidity and machine performance. This data is analyzed for anomaly detection, failure prediction, and operation optimization. Predictive maintenance, thus reduces the idle time of equipment and translates to maximum productivity in the process.
3. Edge Computing
Edge computing is the handling of information much closer to where it was produced rather than being sent up to a central cloud server. In industrial automation, edge computing allows for faster processing of data and also minimizes latency-which is critical for real-time decision-making. Using the computation at the edge, industries can compute data at local levels. This implies faster responses and leaves much lesser data to pass in the networks. It has applications when real-time performance becomes crucial, such as robotic assembly lines and autonomous vehicles.
4. Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is the remote storage, management, and analysis of industrial data that are taken either from a central hub or through allied business machines. Using cloud platforms, an industry can centralize the data, integrate various systems of automation, and draw insights from such voluminous data sets. Cloud computing gives scalability through the easy addition of more devices and systems to automation networks. It also comprises advanced analytics tools whereby industries can make decisions regarding business databases.
5. Wireless Communication
The wireless communication technologies used in M2M communication for industrial automation include the following: Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and LoRaWAN (Long Range Wide Area Network). These technologies achieve the flexibility of deploying and scaling automation systems since they do not require a great deal of wiring. For example, Wi-Fi is used to connect devices on the factory floor to centralized control systems, whereas Bluetooth is mostly used for short-range communication between sensors and controllers. LoRaWAN, however, is more suitable for long-range communication in industrial IoT applications with low-power wide-area connectivity.
Advantages of Telecom & Communication in Industrial Automation
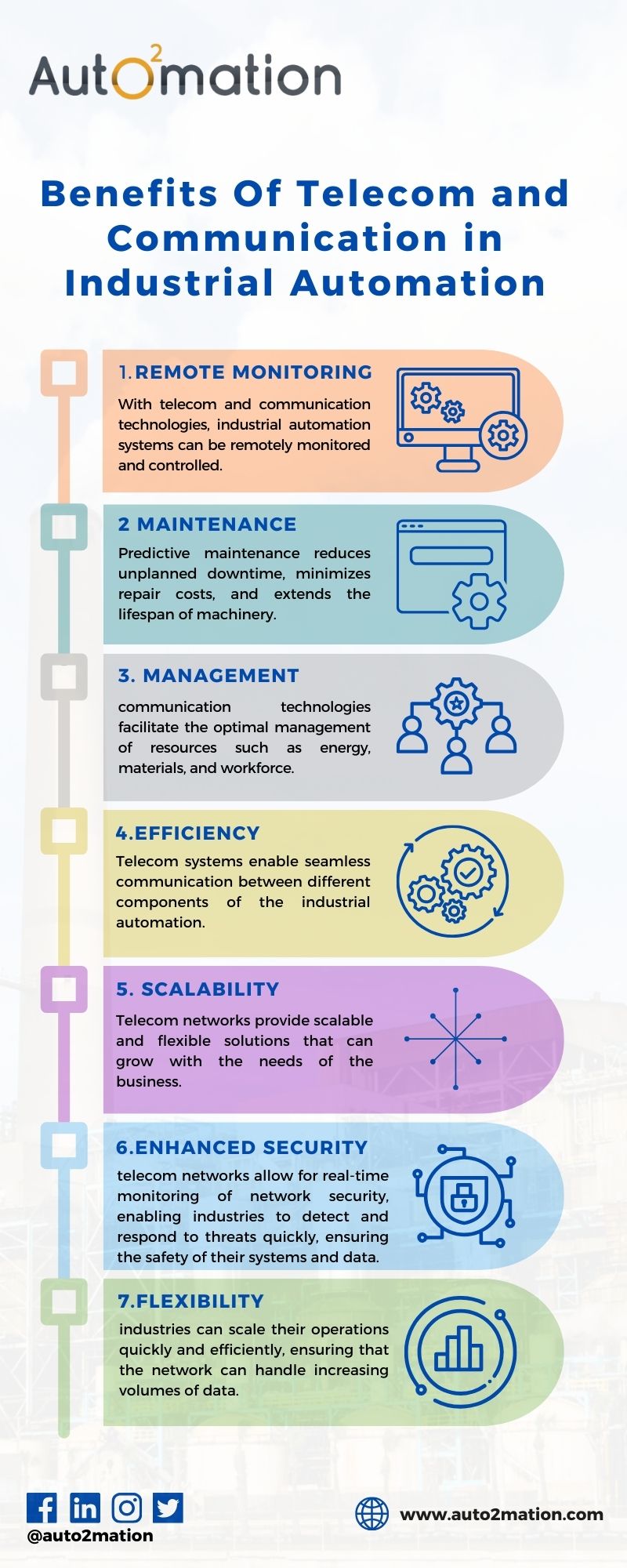
The integration of telecom and communication systems into industrial automation brings many benefits, such as:
1. Improved Efficiency
Telecom systems facilitate more efficient workflows and processes with real-time monitoring and data exchange. The performance of the machine can be adjusted according to real-time data through automation systems. Energy consumption will also be minimized.
2. Reduced Downtime
The predictive maintenance enabled by IoT, including data analytics provided by telecom and communication technologies, can help in recognizing failure before it actually happens. This results in reduced downtime, fewer shutdowns in production, and decreased repairs.
3. Increased Flexibility and Scalability
Wireless communication and IoT integration offer more flexibility in the deployment and scaling of the automation systems. It brings ease to add new devices, machines, and sensors to the already deployed system. Industries can, therefore, easily adapt to changes in needs for the production system and expansion.
4. Safety Improvements
The telecom technologies allow remote monitoring of products, thereby reducing human presence in dangerous environments. This provides a much lower chance of accidents while improving the level of general safety in working environments.
5. Cost Savings
Optimized production processes, reduced equipment downtime, and effective resource management can significantly reduce the operational costs of industries. The high potential for cost savings also comes from the fact that remote monitoring and control systems minimize the number of people required to be present on location.
6. Better Decision-Making
Real-time data and analytics can be very helpful for the industry to make better decisions. The first one is optimization of production schedules, improvement in resource allocation, and overall efficiency of operations.
Future of Industrial Automation with Telecom & Communication
As industrial automation will grow, telecom and communication technologies will be used in the industries widely. Trends and developments in this area in the future are:
1. AI and ML
AI, ML, and telecom networks will take industrial automation further. On one hand, the sheer volume of data coming from IoT devices and communication networks is being processed by AI algorithms to achieve predictive maintenance, quality control, and process optimization.
2. 5G and Beyond
The expansion of 5G networks will make communication even faster and more reliable in industrial environments. Future telecom technologies, like 6G, will further enhance automation capabilities by offering ultra-high speeds, ultra-low latency, and massive device connectivity.
3. Cybersecurity
With more interdependent industries, robust cybersecurity will be needed. Advanced security protocols should be put in place for the telecom and communication technologies in terms of safeguarding sensitive data and the integrity of automated systems.
4. Digital Twins
This means that, in digital twin technology, physical assets, processes, or systems are simulated using virtual replicas. Improvement in monitoring, maintenance, and optimization is made possible due to the capability of telecom networks to exchange real-time data between digital twins and their physical counterparts.
The most effective way to make industrial automation operations more efficient, safe, and cost-effective is to improve the sector through telecom and communication technologies. 5G, IoT, edge computing, and wireless communication will help industries create smarter and more flexible automation systems that spur growth and innovation. As industrial sectors continue to evolve, it will be very evident that telecom and communication will be an integration very much in the position of power for enabling the next wave of industrial transformation. The heightened connectivity, the sharing of real-time data, and the proper decision-making process will heighten the profitability of most industries in this increasingly automated and connected world.





Validate your login
Sign In
Create New Account